Advertisements
Amid the constant evolution of diets and the countless information that bombards us daily, a common question persists: is eating cheese every day bad for your health? At the heart of this question, we find the balance between pleasure and well-being. Modern nutrition, with its advanced research, offers new perspectives on the consumption of foods, including those we love, like cheese 🧀.
This article explores in depth the impact of daily cheese consumption on health, revealing myths and truths in light of current scientific findings. From the most beneficial types of cheese to the recommended amounts, every detail will be covered so that you can make informed decisions and enjoy this delicious treat without guilt.
Advertisements
Learn about the nuances of cheese consumption, from its effects on the heart to possible benefits for bone health. Understand how this food, often seen as a villain, can have a place in a balanced diet. And, of course, discover valuable tips for including cheese in a healthy way in your daily meals. Get ready for a reading that demystifies and clarifies, allowing you to savor each slice with knowledge and pleasure. 🥰
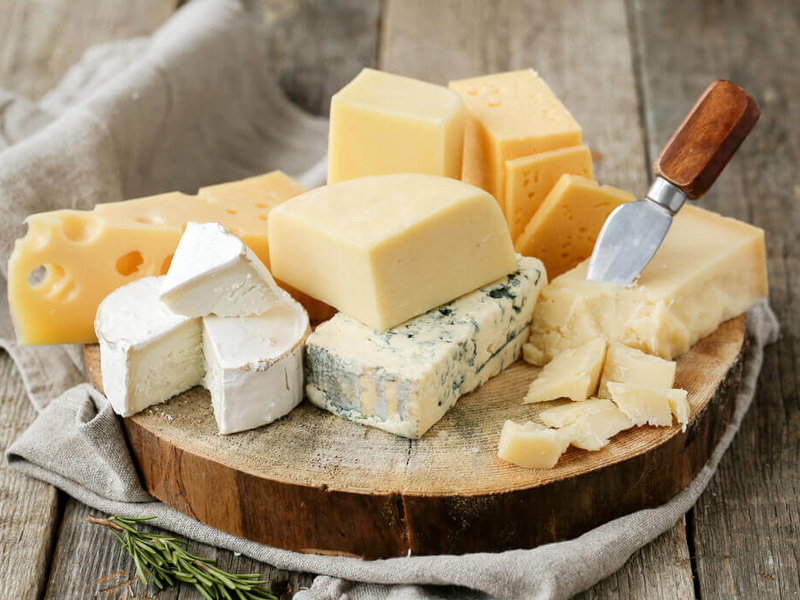

Cheese in the Daily Diet: Myth or Reality?
It’s understandable that many people feel guilty about eating cheese on a daily basis, especially given the stigma that high-fat foods carry. However, modern nutrition offers us a more balanced perspective on cheese consumption. 🧀
Advertisements
To begin, it’s important to understand that cheese is a nutrient-dense food. It contains high-quality protein, calcium, vitamins A and B12, and fatty acids that can be beneficial to your health. But, as with everything in life, moderation is key. Eating too much cheese can contribute to weight gain and heart problems due to its saturated fat content. However, this doesn’t mean that cheese should be banned from your diet.
Modern nutrition teaches us that balance is key. Cheese can be part of a healthy, balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Choosing lower-fat or full-fat varieties of cheese can be a good alternative. Additionally, paying attention to portion sizes and the rest of your daily diet can help keep your cheese intake within healthy limits.
The Nutritional Benefits of Cheese
Before you eliminate cheese from your diet, it’s worth considering the health benefits it can bring. In small amounts, cheese can contribute positively to your nutrition.
Source of Calcium and Bone Health
Calcium is an essential mineral for bone health, and cheese is one of the best dietary sources of this nutrient. Getting enough calcium is especially important for women, who are at higher risk of developing osteoporosis. Including a serving of cheese in your daily diet can help ensure you’re getting enough calcium to maintain strong, healthy bones. 🦴
High Quality Protein
Cheese is an excellent source of high-quality protein, which is vital for building and repairing body tissues. Protein also plays an important role in strengthening the immune system and maintaining healthy muscles. For those following a vegetarian diet, cheese can be a valuable source of protein.
Recommended Articles
Rich in Vitamins and Minerals
In addition to calcium, cheese provides a variety of essential vitamins and minerals. Vitamin B12, which is found in good amounts in cheese, is important for neurological function and the formation of red blood cells. Cheese is also a source of vitamin A, which is crucial for eye health and immune function.
Demystifying Fat in Cheese
Concerns about the fat content of cheese are one reason many people are hesitant to eat it on a daily basis. However, understanding the types of fat in cheese can help you make more informed dietary decisions.
Saturated Fat: Villain or Ally?
Cheese contains saturated fat, which has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. However, recent studies suggest that the link between saturated fat and heart disease is not as clear-cut as previously thought. In fact, some research suggests that full-fat dairy may even have a protective effect on the heart.
The key is moderation. Eating cheese as part of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains can minimize the potential risks associated with saturated fat.
Choosing the Right Type of Cheese
Not all cheeses are created equal. Lower-fat cheese varieties, such as cottage cheese or ricotta, can be healthy alternatives for those looking to reduce their saturated fat intake. Aged cheeses, such as Parmesan or Cheddar, offer intense flavors and can be used in smaller quantities to add flavor to dishes without compromising health.
The Role of Cheese in Modern Diets
Cheese can be healthily incorporated into many modern dietary approaches, as long as it is consumed wisely.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, known for its cardiovascular health benefits, includes cheese as part of its diet. However, in this diet, cheese is consumed in moderation and in conjunction with other healthy foods, such as olive oil, fish, and fresh vegetables. This eating pattern shows that cheese can be part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Low-Carb and Keto Diet
For those following a low-carb or ketogenic diet, cheese can be an excellent option because it is rich in protein and fat, but contains few carbohydrates. In these types of diets, cheese can help increase satiety and provide necessary nutrients without compromising dietary goals.
- Recommended cheeses: Brie, Camembert, Blue Cheese
- Moderation: Important to not exceed caloric intake
Enjoying Cheese Without Guilt
For many, cheese is not only a source of nutrients, but also a source of gastronomic pleasure. Knowing that it is possible to enjoy cheese without guilt can be a relief.
Balancing Flavors and Health
Cheese can be used as a balancing element in healthy meals. For example, adding a little grated Parmesan cheese to a salad or using slices of fresh cheese on a vegetable sandwich can increase the flavor and nutritional value of your meal without compromising your health.
Conscious Portions
Paying attention to portions is essential to include cheese in your daily diet in a healthy way. Small portions of cheese with intense flavors can satisfy your palate and provide a pleasant experience without overdoing it.
- Suggested serving: 30 to 50 grams per day
- Combinations: Fruits, nuts and whole grains
With this information, we hope you can feel more confident and at ease when including cheese in your diet. After all, health is about balance, pleasure and informed choices. 🧀✨
Conclusion
In conclusion, the myth that eating cheese every day is bad for you has been largely debunked by modern nutrition 🧀. Although cheese has historically been seen as a villain due to its fat and sodium content, today we know that it offers several nutritional benefits. For example, cheese is an excellent source of calcium, which is essential for bone health, and contains proteins that help build and repair muscles. However, as with any food, moderation is key. Therefore, instead of eliminating cheese from your diet, consider adjusting your portions and opting for varieties with lower fat and sodium content, such as cottage cheese or ricotta. In addition, it is crucial to include cheese consumption in a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. This way, you can enjoy your favorite dishes without feeling guilty 😊. By taking these precautions, cheese can be a delicious addition to your daily diet. In short, with moderation and informed choices, cheese doesn’t have to be a forbidden food, but rather a tasty and nutritious part of your daily diet 🍽️. So don’t be afraid to enjoy this classic ingredient in your daily diet!